French Indochina
| Full Name | 28 Indochinese Federation | |
| Alliance | Neutral or Non-Belligerent | |
| Possessing Power | France | |
| Entry into WW2 | 23 Sep 1940 | |
| Population in 1939 | 24,568,000 | |
| Civilian Deaths in WW2 | 1,500,000 |
Contributor: C. Peter Chen
ww2dbaseFrench involvement in Southeast Asia began in Sep 1858 when French troops, with Spanish assistance, attacked the port cities of Da Nang and Saigon in Nguyen Dynasty Vietnam. In 1863, Cambodian King Norodom voluntarily submitted his kingdom to France as a protectorate. The series of French territorial gains in the subsequent years resulted in the formation of French Indochina in 1887 as a federation of colonial holdings. Initially it included present day Vietnam and Cambodia; administratively, the Vietnamese region was broken up to Tokin, Annam, and Cochinchina. The capital was seated in Saigon, Cochinchina. Laos entered the federation in 1893 after the French military defeated Siam. The treaty port of Kouang-Tchéou-Wan (Chinese: Guangzhouwan) in southern China was forcibly leased from Qing Dynasty China in 1899 and was governed as a part of French Indochina. In 1902, the capital was moved to Hanoi, Tonkin. Additional territory was gained from Siam in the early 1900s. In 1939, the capital was moved to Da Lat, Annam. The coastal area provided tea, rice, coffee, pepper, coal, zinc, tin, and rubber for the French empire, while further inland, the Laos region provided some timber; rubber, in particular, elevated French Indochina's value, especially after the rise in the usage of automobiles. Saigon was the main transportation and commercial center for French Indochina, becoming the sixth busiest port in the entire French empire by 1937. The Trans-Indochinois railway, which connected Hanoi and Saigon, opened in 1936. At the eve of WW2, the population of French Indochina was roughly 7,784,000 in Tonkin, 8,000,000 in Annam, 4,484,000 Cochinchina, 3,000,000 in Cambodia, and 1,300,000 in Laos for a total of about 24,568,000.
ww2dbaseIn the European War, France was defeated by Germany. Significantly weakened, France(ie. Vichy France) attempted to remain non-belligerent in the ongoing conflict, but to little success. The Japanese military demanded, and was given, permission to establish a military mission in Tonkin in Jun 1940. In Aug 1940, Japan further demanded the right to use airfields in other areas of French Indochina, and the French dragged on the negotiations as long as they could while they looked to Britain and the United States for support, which France would receive little. On 5 Sep, angered by the repeated delays, Japanese troops invaded French Indochina. The French admitted defeat on 25 Sep 1940, starting a period in which French Indochina remained a French possession in name only, while the Japanese wielded real power behind the scenes. Taking advantage of the situation, Thai troops provoked French Indochina as well beginning in Oct 1940, escalating to the Franco-Thai War. The Japanese interfered and negotiated an end, which saw Thailand regaining the territories it had lost to France in the early 1900s. The Japanese aggression against French Indochina became the final straw that led to the American decision to ban the export for strategic materials to Japan. French Indochina as a whole played an important part of early WW2 as it cut off a supply route for the Chinese. When the Pacific War broke out in Dec 1941, Cochinchina served as a jump off point for Japanese invasion troops for British Malaya.
ww2dbaseJapan controlled the three colonies in Vietnam with French puppets until 9 Mar 1945, when the Japanese took direct control. The Americans and the Chinese supported the Viet Nam Doc Lap Dong Minh Hoi (Vietnamese Independence Society) resistance movement in French Indochina, which had communist members, but the movement did not uphold a communist philosophy. Shortly after, the Soviet Union would become a strong supporter as well. The society was better known in the West by its shortened name, Viet Minh. By 1944, Viet Minh would claim a membership of 500,000, 200,000 of which in Tokin, 150,000 in Annam, and 150,000 in Cochinchina. When the war ended, captured Japanese weapons and facilities were handed over to the Viet Minh. The defeat of the common enemy caused the various factions within the society to break apart, each proclaiming an independent Vietnam. The return of the French did not unite the separate movements. Ultimately it would be the communist faction under Ho Chi Min that would achieve victory over the following decades.
ww2dbaseCambodia was occupied by about 8,000 Japanese troops throughout the war. The French remained in nominal control of Cambodia until 9 Mar 1945, when King Norodom Sihanouk declared the nominally independent Kingdom of Kampuchea with Japanese support. The French colonial administration returned to Cambodia after WW2. Cambodia would gain independence when French Indochina was made defunct in 1953, and King Norodom Sihanouk would remain its monarch until 1955 (he would remain an influence leader for many decades to come).
ww2dbaseLaos was under the influence of both Japan and Thailand during the war. Several resistance movements were formed during this time, including one supported by the French. On 8 Apr 1945, King Sisavang Vong declared the nominally independent Kingdom of Laos; Crown Prince Savang Vatthana would soon head for the mountains to form another anti-Japanese movement. After the war, King Sisavang Vong willingly subjugated himself under the returning French, which triggered a brief power struggle with the Lao Issara nationalists. King Sisavang Vong regained power in Apr 1946. Laos would gain independence after the end of French Indochina in 1953, and King Sisavang Vong would remain the monarch until his death in Oct 1959.
ww2dbaseAltogether, the region suffered somewhere between 1,000,000 to 2,000,000 deaths during the war years, the majority of which from famine and mistreatment by the Japanese.
ww2dbaseSource: Wikipedia
Last Major Update: Oct 2014
| People | ||
| Bao Dai | Phetsarath, Ratanavongsa | |
| Meynier, Katiou | Tran, Trong Kim | |
| Events Taken Place in French Indochina | ||
| Indochina Campaign | 23 Sep 1940 - 26 Sep 1940 | |
| Franco-Thai War | 1 Oct 1940 - 31 Jan 1941 | |
| Raid into the South China Sea | 10 Jan 1945 - 20 Jan 1945 | |
| Japan's Surrender | 14 Aug 1945 - 2 Sep 1945 | |
Photographs
 |  |  |  |
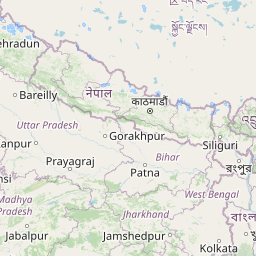
French Indochina in World War II Interactive Map
Please consider supporting us on Patreon. Even $1 per month will go a long way! Thank you. Please help us spread the word: Stay updated with WW2DB: |

- » US State Lawmaker John Winter Caught Using Racial Slur "Jap" and Apologized (11 Jun 2025)
- » Köln/Cologne Evacuated After Discovery of WW2 Bombs (4 Jun 2025)
- » US Women's Army Corps "Six Triple Eight" Awarded with Congressional Gold Medal (30 Apr 2025)
- » Race, Holocaust, and African-American WW2 Histories Removed from the US Naval Academy Library (7 Apr 2025)
- » US Government Plans to Purge WW2 Information (17 Mar 2025)
- » See all news
 |
- » 1,176 biographies
- » 337 events
- » 44,927 timeline entries
- » 1,245 ships
- » 350 aircraft models
- » 207 vehicle models
- » 376 weapon models
- » 123 historical documents
- » 261 facilities
- » 470 book reviews
- » 28,467 photos
- » 365 maps
Winston Churchill
Please consider supporting us on Patreon. Even $1 a month will go a long way. Thank you!
Or, please support us by purchasing some WW2DB merchandise at TeeSpring, Thank you!