US Pacific Islands
| Alliance | Allies - Minor Member Nation or Possession | |
| Possessing Power | United States | |
| Entry into WW2 | 7 Dec 1941 |
Contributor: C. Peter Chen
ww2dbaseJohnston Atoll
ww2dbaseIn Aug 1939, the United States Congress authorized funding to upgrade or build naval air facilities across the various US territories in the Pacific Ocean. Some of this funding were directed at Johnson Atoll, which was a coral atoll of two main islands about 720 miles southwest of Oahu in the US Territory of Hawaii. The work at the atoll temporarily halted during the opening phases of the Pacific War as it was bombarded by Japanese submarines, but it would eventually resume. In Jul 1942, all civilian contractors at Johnston Atoll were replaced by US Navy Construction Battalion personnel. By 1943, it had undoubtedly become an important stop for air transports for the US military. The main island of Johnston Island, originally only 40 acres in size, would grow to 160 acres, which was a testament of the atoll's importance.
ww2dbaseMidway Atoll
ww2dbaseThe Aug 1939 base expansion plan included funding to upgrade or build naval air facilities at the coral atoll of Midway. Initially, the US Army developed Midway as to be a seaplane base; this work was done in 1940. Before the Pacific War began, a small naval hospital was also built. Over the course of the war, however, the strategic location of Midway Atoll meant that she would also take on the role of a major submarine base and a major air station. The facilities at Midway Atoll received minor damage during the Jun 1942 Battle of Midway, which resulted from a Japanese attempt to take the atoll, but most of the action took place far out to sea to the northwest. After the end of the Pacific War, Midway was briefly decommissioned in 1950, but became an active base once again during the Korean War. The atoll was declared a National Wildlife Refuge in 1988, and the naval base officially closed on 10 Sep 1993. On 31 Oct 1996, jurisdiction of the atoll was transferred from the US Navy to the US Department of the Interior.
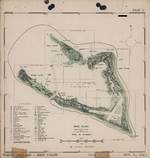
ww2dbasePalmyra Atoll
ww2dbasePalmyra Atoll was located 960 miles south of the Hawaiian Islands; it was a member of the Northern Line Islands. The Aug 1939 base expansion plan included funding to upgrade or build naval air facilities at Palmyra Atoll. In the decades after the war, Palmyra gradually lost its importance, especially given that it had no indigenous population. The Nature Conservancy purchased most of the atoll in Dec 2000 for coral reef conservation and research. The Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument law established in 2009 reaffirmed US Department of the Interior's jurisdiction over Palmyra.
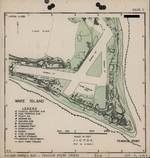
ww2dbaseWake Atoll
ww2dbaseWake was an atoll consisted of three islands, Wake, Peale, and Wilkes. The United States took control of this uninhabited territory in 1899, and it was not until 1935, when the Pan American Airways established a small village there, when the atoll became inhabited. The military build-up across the Pacific Ocean included Wake. On 19 Aug 1941, the first permanent military garrison was established on Wake, which consisted of 449 US Marines. The Pacific War broke out when Wake Atoll's construction work was only about 65% complete. The facilities on the island was subjected to Japanese aerial bombardment beginning on 8 Dec 1941, within hours of the Pearl Harbor attack (Wake was located west of the International Date Line), and a Japanese invasion force took control of the atoll on 23 Dec. Wake would remain under Japanese control for the remainder of the war. Throughout the war, Wake was subjected to American aerial attacks. After a particularly successful bombardment, Japanese Navy Captain Shigematsu Sakaibara ordered the execution of the 98 prisoners of war present on the island; Sakaibara would later be found guilty of war crimes and sentenced to death. Some time in 1945, the Japanese occupation hunted to extinction the flightless bird species Wake Island Rail, the atoll's only native species, as food for the garrison after the Americans blockaded the atoll. The Americans took control of the atoll on 4 Sep 1945 at the end of the Pacific War. After the war, United States Army Space and Strategic Defense Command was given jurisdiction of the atoll. During the Vietname War, between Apr and Aug 1975, Wake hosted a refugee camp for more than 8,000 Vietnamese refugees. Today Wake Atoll is jointly controlled by the United States Air Force and the United States Department of the Interior.
ww2dbaseSources:
United States Navy Naval History and Heritage Command
Wikipedia
Last Major Update: Mar 2013
| Events Taken Place in US Pacific Islands | ||
| Battle of Wake Island | 11 Dec 1941 - 23 Dec 1941 | |
| Battle of Midway and the Aleutian Islands | 4 Jun 1942 - 7 Jun 1942 | |
| Facilities | ||
| Midway Bases | Air Base, Navy Base | |
Weather
WW2-Era Weather Data for US Pacific Islands
Photographs
 |  |  |  |
 |  |
US Pacific Islands in World War II Interactive Map
Please consider supporting us on Patreon. Even $1 per month will go a long way! Thank you. Please help us spread the word: Stay updated with WW2DB: |

- » Wreck of Teruzuki Found (27 Jul 2025)
- » USS Orlean's Bow Found (22 Jul 2025)
- » The Emperor of Japan Planned to Honor WW2-era Japanese POWs in Mongolia (4 Jul 2025)
- » US State Lawmaker John Winter Caught Using Racial Slur "Jap" and Apologized (11 Jun 2025)
- » US Government Plans to Purge WW2 Information (17 Mar 2025)
- » See all news
 |
- » 1,181 biographies
- » 337 events
- » 45,111 timeline entries
- » 1,247 ships
- » 350 aircraft models
- » 207 vehicle models
- » 376 weapon models
- » 123 historical documents
- » 261 facilities
- » 470 book reviews
- » 28,476 photos
- » 365 maps
Winston Churchill, 1935
Please consider supporting us on Patreon. Even $1 a month will go a long way. Thank you!
Or, please support us by purchasing some WW2DB merchandise at TeeSpring, Thank you!