Deutsche Werke Kiel
| Type | 207 Shipyard | |
| Historical Name of Location | Kiel, Schleswig-Holstein, Germany | |
| Coordinates | 54.319523000, 10.158281000 |
Contributor: Al Griffis
ww2dbaseIn 1867, Königliche Werft Kiel was founded in Kiel, Germany. Slip I was built between 1868 and 1875, and slip II between 1870 and 1875. In 1871, the shipyard was renamed Kaiserliche Werft Kiel as the German Empire was proclaimed, and a naval arsenal at the same location was planned. Between 1871 and 1879, dry docks I through IV were built. In 1906, slip I was widened. In Aug 1918, it was assigned to the Ministry of Finance. After WW1, the Weimar Republic became its owner. Between 1919 and 1924, Deutsche Werke Kiel produced the Ortgies semi-automatic pistol. In May 1925, it became the public limited company Deutsche Werke Kiel AG. Between 1925 and 1933, it constructed ships for the civilian sector; with the Nazi rise to power in 1933, it slowly turned to the construction of warships. In 1935, it was decided that a third slip was necessary; the construction for this began in 1937 and was completed shortly after the start of the European War. In Feb 1940, a 500-ton floating drydock which was sunk during recent operations was raised and repaired. At the peak of operations, Deutsche Werke Kiel employed over 2,000 workers. As the European War went on, however, it suffered serious damage from Allied bombings. In Mar 1945, an order was given to destroy the shipyard facilities before Allied capture, but the orders were not obeyed. After the war, it was reorgnized as Maschinenbau Kiel, and in 1955 the shipyard facilities were purchased by Howaldtswerke.
ww2dbaseSource: Wikipedia
Last Major Update: Oct 2019
Ships Constructed at Deutsche Werke Kiel
| Ship Name | Yard No | Slip/Drydock No | Ordered | Laid Down | Launched | Commissioned |
| U-1235 | ||||||
| U-452 | III | |||||
| U-453 | III | |||||
| U-454 | III | |||||
| U-459 | III | |||||
| U-460 | III | |||||
| U-461 | III | |||||
| U-462 | III | |||||
| U-463 | III | |||||
| U-464 | III | |||||
| Franken | II | 18 Feb 1937 | 8 Jun 1939 | 17 Mar 1943 | ||
| Karlsruhe | 207 | II | 8 Apr 1925 | 27 Jul 1926 | 20 Aug 1927 | 6 Nov 1929 |
| Deutschland | 219 | I | 10 Aug 1928 | 5 Feb 1929 | 19 May 1931 | 1 Apr 1933 |
| Nürnberg | 234 | II | 16 Jun 1933 | 4 Nov 1933 | 6 Dec 1934 | 2 Nov 1935 |
| Gneisenau | 235 | I | 25 Jan 1934 | 14 Feb 1934 | 8 Dec 1936 | 21 May 1938 |
| Z1 Leberecht Maass | 242 | Drydock I | 7 Apr 1934 | 10 Oct 1934 | 18 Aug 1935 | 14 Jan 1937 |
| Z2 Georg Thiele | 243 | Drydock II | 7 Apr 1934 | 25 Oct 1934 | 18 Aug 1935 | 27 Feb 1937 |
| Z3 Max Schultz | 244 | Drydock III | 7 Apr 1934 | 2 Jan 1935 | 30 Nov 1935 | 8 Apr 1937 |
| Z4 Richard Beitzen | 245 | Drydock IV | 7 Apr 1934 | 7 Jan 1935 | 30 Nov 1935 | 13 May 1937 |
| U-1 | 236 | 117a r | 8 Feb 1935 | 11 Feb 1935 | 15 Jun 1935 | 29 Jun 1935 |
| U-2 | 238 | 117b r | 8 Feb 1935 | 11 Feb 1935 | 1 Jul 1935 | 25 Jul 1935 |
| U-3 | 239 | 117b l | 8 Feb 1935 | 11 Feb 1935 | 19 Jul 1935 | 6 Aug 1935 |
| U-4 | 237 | 117a l | 8 Feb 1935 | 11 Feb 1935 | 31 Jul 1935 | 17 Aug 1935 |
| U-5 | 241 | 117c l | 8 Feb 1935 | 11 Feb 1935 | 14 Aug 1935 | 31 Aug 1935 |
| U-6 | 240 | 117c r | 8 Feb 1935 | 11 Feb 1935 | 21 Aug 1935 | 7 Sep 1935 |
| U-13 | 248 | 117a r | 2 Feb 1935 | 20 Jun 1935 | 9 Nov 1935 | 30 Nov 1935 |
| U-14 | 249 | 117b r | 2 Feb 1935 | 6 Jul 1935 | 28 Dec 1935 | 18 Jan 1936 |
| U-16 | 251 | 117a l | 2 Feb 1935 | 5 Aug 1935 | 28 Apr 1936 | 16 May 1936 |
| Blücher | 246 | II | 30 Oct 1934 | 15 Aug 1935 | 8 Jun 1937 | 20 Sep 1939 |
| U-15 | 250 | 117b l | 2 Feb 1935 | 24 Sep 1935 | 15 Feb 1936 | 7 Mar 1936 |
| Graf Zeppelin | 252 | I | 16 Nov 1935 | 28 Dec 1936 | 8 Dec 1938 | |
| U-57 | 255 | I | 17 Jun 1937 | 14 Sep 1937 | 3 Sep 1938 | 29 Dec 1938 |
| U-56 | 255 | 17 Jun 1937 | 21 Sep 1937 | 3 Sep 1938 | 26 Nov 1938 | |
| U-58 | 256 | 17 Jun 1937 | 28 Sep 1937 | 12 Oct 1938 | 4 Feb 1939 | |
| U-59 | 257 | 17 Jun 1937 | 5 Oct 1937 | 12 Oct 1938 | 4 Mar 1939 | |
| U-60 | 259 | 21 Jul 1937 | 1 Oct 1938 | 1 Jun 1939 | 22 Jul 1939 | |
| U-61 | 260 | 21 Jul 1937 | 1 Oct 1938 | 15 Jun 1939 | 12 Aug 1939 | |
| U-62 | 261 | 21 Jul 1937 | 2 Jan 1939 | 16 Nov 1939 | 21 Dec 1939 | |
| U-63 | 262 | 21 Jul 1937 | 2 Jan 1939 | 6 Dec 1939 | 18 Jan 1940 | |
| O (Planned) | 265 | I | 8 Aug 1939 | 5 Jan 1939 * | 1 Jan 1941 * | 1 Jan 1943 * |
| M (Planned) | 263 | II | 24 May 1938 | 1 Sep 1939 * | 1 Sep 1941 * | 1 Oct 1942 * |
| U-137 | 266 | I | 25 Sep 1939 | 16 Nov 1939 | 18 May 1940 | 15 Jun 1940 |
| U-138 | 267 | I | 25 Sep 1939 | 16 Nov 1939 | 18 May 1940 | 27 Jun 1940 |
| U-140 | 269 | I | 25 Sep 1939 | 16 Nov 1939 | 28 Jun 1940 | 7 Aug 1940 |
| U-139 | 268 | I | 25 Sep 1939 | 20 Nov 1939 | 28 Jun 1940 | 7 Aug 1940 |
| U-141 | 270 | I | 25 Sep 1939 | 12 Dec 1939 | 27 Jul 1940 | 21 Aug 1940 |
| U-142 | 271 | I | 25 Sep 1939 | 12 Dec 1939 | 27 Jul 1940 | 4 Sep 1940 |
| U-143 | 272 | III | 25 Sep 1939 | 3 Jan 1940 | 10 Aug 1940 | 18 Sep 1940 |
| U-144 | 273 | III | 25 Sep 1939 | 10 Jan 1940 | 24 Aug 1940 | 2 Oct 1940 |
| U-145 | 274 | III | 25 Sep 1939 | 29 Mar 1940 | 21 Sep 1940 | 16 Oct 1940 |
| U-146 | 275 | III | 25 Sep 1939 | 30 Mar 1940 | 21 Sep 1940 | 30 Oct 1940 |
| U-147 | 276 | III | 25 Sep 1939 | 10 Apr 1940 | 16 Nov 1940 | 11 Dec 1940 |
| U-148 | 277 | III | 25 Sep 1939 | 10 Apr 1940 | 16 Nov 1940 | 28 Dec 1940 |
| U-149 | 278 | I | 25 Sep 1939 | 25 May 1940 | 19 Oct 1940 | 13 Nov 1940 |
| U-150 | 279 | I | 25 Sep 1939 | 25 May 1940 | 19 Oct 1940 | 27 Nov 1940 |
| U-151 | 280 | I | 25 Sep 1939 | 6 Jul 1940 | 14 Dec 1940 | 15 Jan 1941 |
| U-152 | 281 | I | 25 Sep 1939 | 6 Jul 1940 | 14 Dec 1940 | 29 Jan 1941 |
| K (Planned) | 264 | III | 25 May 1939 | 1 Oct 1940 * | 1 Oct 1942 * | 1 Apr 1944 * |
| P1 (Planned) | I | 1 May 1941 * | 1 May 1943 * | 1 Oct 1944 * | ||
| O (Planned) | 264 | II | 24 May 1938 | 1 Oct 1941 * | 1 Oct 1943 * | 1 Nov 1944 * |
| P7 (Planned) | III | 1 May 1943 * | 1 May 1945 * | 1 Oct 1946 * | ||
| U-491 | III | 22 Sep 1942 | 31 Jul 1943 | |||
| U-492 | III | 22 Sep 1942 | 21 Aug 1943 | |||
| U-493 | III | 22 Sep 1942 | 25 Sep 1943 | |||
| U-494 | III | 14 Dec 1943 | 1 Nov 1943 | |||
| M (Planned) | 263 | I | 1 Oct 1941 | 1 Jan 1944 * | 1 Jul 1945 * | 1 Jul 1946 * |
| R (Planned) | II | 1 Dec 1941 | 1 Jun 1944 * | 1 Dec 1945 * | 1 Dec 1946 * | |
| SP16 (Planned) | III | 1 Jun 1945 * | 1 Sep 1946 * | 1 Apr 1948 * | ||
| SP20 (Planned) | I | 1 Sep 1945 * | 1 Dec 1946 * | 1 Jun 1948 * | ||
| Q2 (Planned) | II | 1 Jun 1943 | 1 Feb 1946 * | 1 Sep 1947 * | 1 Sep 1948 * |
* Projected dates; not actual
Slip/Drydock Utilization
[Con]: Construction; [FO]: Fitting Out
Deutsche Werke Kiel Interactive Map
Photographs
 |  |  |  |
Maps
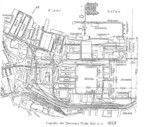 |
Deutsche Werke Kiel Timeline
| 28 May 1925 | The former Kaiserliche Werft Kiel in Germany became the public limited company Deutsche Werke Kiel AG. |
| 19 May 1931 | The German pocket battleship Deutschland was launched by Deutsche Werke Kiel, Germany. |
| 3 Mar 1935 | The keel of the German battlecruiser Gneisenau was laid down in Dry Dock I of Deutsche Werke Kiel, Germany. |
| 25 May 1935 | Deutsche Werke Kiel AG in Germany began planning the construction of a third slip. |
| 13 Dec 1935 | Representatives of Deutsche Werke Kiel AG in Germany met with Erich Raeder on the construction of a third slip. |
| 28 Dec 1936 | The keel of Graf Zeppelin was laid down in Dry Dock I of Deutsche Werke Kiel, Germany. |
| 1 Feb 1937 | The construction work for slip III at Deutsche Werke Kiel AG in Germany began. |
| 21 Sep 1937 | The keel of U-56 was laid down at Deutsche Werke, Kiel, Germany. |
| 3 Sep 1938 | U-56 was launched at Deutsche Werke, Kiel, Germany. |
| 8 Dec 1938 | Graf Zeppelin was launched by Deutsche Werke Kiel in Kiel, Germany. |
| 8 Jun 1939 | Franken was launched at the Deutsche Werke Kiel shipyard in Kiel, Germany. |
| 19 Sep 1939 | The work on light cruiser M ceased at Deutsche Werke Kiel, Germany. |
| 19 Sep 1939 | The construction of Graf Zeppelin was halted temporarily as Erich Raeder and Hermann Göring competed for resources. |
| 23 Sep 1939 | The construction work for slip III at Deutsche Werke Kiel AG in Germany completed. |
| 29 Apr 1940 | The work on carrier Graf Zeppelin was stopped. |
| 8 Jul 1940 | British bombers attacked German heavy cruiser Lützow in dock at Kiel, Germany. Lützow, under repair for extensive torpedo damage to her stern caused by HMS Spearfish on 11 Apr 1940, was hit by a bomb that failed to detonate. |
| 8 Mar 1941 | Battleship Bismarck exited the Kiel Canal and entered Dock C of Deutsche Werke Kiel, Germany. |
| 25 Jul 1941 | British bombers took off at 2230 hours on the previous day, reaching Kiel, Germany at about 0145 hours on this date; bombs were dropped on the Deutsche Werke shipyard facilities; surviving attacks landed at their bases in Britain at about 0600 hours. On the same day, Bombers of British No. 102 Squadron RAF attacked Hanover, Germany after sundown. |
| 7 Aug 1941 | After dark, 84 British aircraft were launched to attack Essen, Germany (108 tons of high explosive bombs and 5,720 incendiary bombs were dropped, damaging the Krupp coke oven batteries), 31 launched against Hamm (damaging rail marshalling yard), 32 launched against Dortmund, 88 launched against Kiel (104 tons of high explosive bombs and 4,836 incendiary bombs were dropped, damaging Deutsche Werke Shipyards), and a number of bombers were launched against Hamburg (poor visibility and results were not observed). |
| 26 Feb 1942 | 49 British RAF bombers attacked Gneisenau in the drydock at Kiel, Germany. A bomb penetrated the armored deck, triggering a detonation in the forward turret which caused great damage to entire bow section of the ship; 112 were killed, 21 were wounded. |
| 5 Dec 1942 | Graf Zeppelin was towed to Kiel, Germany. |
| 11 Mar 1945 | While under repair at Deutsche Werke shipyard in Kiel, Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, Emden suffered damage on the forward deck and port torpedo launchers from Allied aerial incendiary bombs. |
| 25 Mar 1945 | An order was given to destroy the facilities of Deutsche Werke Kiel in Germany before Allied capture, but it would not be obeyed. |
| 3 Apr 1945 | While under repair at Deutsche Werke shipyard in Kiel, Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, Emden had her forward funnel destroyed by a direct hit of an Allied aerial bomb. |
| 9 Apr 1945 | While under repair at Deutsche Werke shipyard in Kiel, Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, Emden was damaged by a near miss of a bomb from an Allied aircraft. |
| 13 Apr 1945 | While under repair at Deutsche Werke shipyard in Kiel, Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, Emden was damaged by Allied aircraft. |
| 14 Apr 1945 | In the morning, damaged Emden was towed from Deutsche Werke shipyard in Kiel, Schleswig-Holstein, Germany to the nearby Heikendorfer Bucht. After observing a 15-degree list to port due to flooding, her crew sealed the hull and beached her to prevent sinking. |
Please consider supporting us on Patreon. Even $1 per month will go a long way! Thank you. Please help us spread the word: Stay updated with WW2DB: |
Visitor Submitted Comments
16 Jun 2025 01:17:53 PM
Interesting info, I miss info about Jessenitz labor camp, Kriegsmarinearsenal, and munition factory for Rüstungsindustrie during wWO-2, PART OF DWK, where hundreds of forced labourers worked from 1941-45 from Netherland, France, Italy and Russia. Can you help me with info? Thank you
All visitor submitted comments are opinions of those making the submissions and do not reflect views of WW2DB.

Kiel, Schleswig-Holstein, Germany
Latitude-Longitude:
54.3195, 10.1583
- » 1,182 biographies
- » 337 events
- » 45,119 timeline entries
- » 1,249 ships
- » 350 aircraft models
- » 207 vehicle models
- » 376 weapon models
- » 123 historical documents
- » 261 facilities
- » 470 book reviews
- » 28,412 photos
- » 365 maps
Lt. Gen. Lewis B. "Chesty" Puller, at Guadalcanal
Please consider supporting us on Patreon. Even $1 a month will go a long way. Thank you!
Or, please support us by purchasing some WW2DB merchandise at TeeSpring, Thank you!
6 Apr 2023 09:11:19 AM
I am missing information about forced labourers at DWK during WOII.
Also, this area must have been heavily bombarded during the war.
That information is also not clear