Dutch East Indies
| Alliance | Allies - Minor Member Nation or Possession | |
| Possessing Power | Netherlands | |
| Entry into WW2 | 8 Dec 1941 | |
| Population in 1939 | 60,727,233 | |
| Civilian Deaths in WW2 | 4,000,000 |
Contributor: C. Peter Chen
ww2dbaseThe Dutch East Indies, or Netherlands East Indies, was formed as a colony of the Netherlands in 1800 when the country nationalized the Dutch East India Company. It expanded to the territories seen on the eve of WW2 with the annexation of the Bird's Head Peninsula in western New Guinea in 1920. In 1941, the Dutch East Indies produced large quantities of coffee, tea (20% of the world's supply), cacao, coconut (25% of the world's supply), sugar, pepper, tobacco, rubber (35% of the world's supply), quinine (most of the world's supply), and oil (significant portion of the world's supply). The islands were the Netherland's main source of raw materials; very little industry was developed in the Dutch East Indies. In the 1900s the Dutch began to implement better flood control, education, and other programs to help the colonial subjects, but ultimately these programs were not effective. As main the interest for the Dutch colonial administration for the colony was trade, the Dutch language was never forced upon the local population; instead, the popular Riau dialect of Malay language was adopted as the official language so that trade would not be hindered; this official language would later involve into the modern Indonesian language.
ww2dbaseThe Netherlands declared war on Japan on 8 Dec 1941, and the Dutch forces fought against the Japanese under the American-British-Dutch-Australian Command (ABDACOM) structure. Celebes was invaded during the night of 10 to 11 Jan 1942, while Tarakan, Borneo was taken in mid-Jan. In late Feb, Japanese naval forces defeated the Allied fleet at the Java Sea while Japanese Army troops landed on Java. The Dutch ground forces, though slightly better armed than their counterparts in Europe during the German invasion in 1940, were unable to stop the Japanese invasion and surrendered on 8 Mar 1942. This ended 300 years of Dutch influence in the South Pacific.
ww2dbaseA small number of Dutch servicemen remained in the theater and participated in various campaigns in the Pacific War. Dutch pilots who fled to Australia in early 1942 formed the No. 18 Squadron RAAF in Apr 1942 and No. 120 Squadron RAAF in Dec 1943 to continue the fight, for example. Dutch soldiers also played a part in the 1945 invasion of Borneo.
ww2dbaseWhile most colonial members of the Dutch forces in Dutch East Indies were released back into the population, thousands of both military and civilian Dutch were placed in prison camps; some of them were later deported to Japan, Thailand, Malaya, and Burma as forced laborers. The Japanese were initially welcomed by the local populations, who viewed Japan as a friendly neighboring power who had liberated the Pacific Islands from European colonialism. In Jul 1942, Indonesian nationalist leader Sukarno publicly offered support for the Japanese war effort, for example, and his organization would continue to receive Japanese support throughout the entire occupation. Certain Japanese action in the islands, however, revealed their true intentions. Thousands among the local population were conscripted as forced laborers, while raw materials and food were shipped abroad, causing material shortages and starvation.
ww2dbaseThe Japanese occupation administration divided the Dutch East Indies into three regions for defense purposes. Sumatra was defended by the 25th Army, Java and Madura by the 16th Army, and Borneo and the remaining major islands by the 2nd South Fleet of the Japanese Navy. The Allied campaign across the South Pacific ultimately bypassed most of the populous islands except for New Guinea and Borneo, thus most of the population centers were saved from destruction but remained under Japanese rule until the end of the Pacific War.
ww2dbaseAfter the war, most of the 300,000 Japanese were deported back to Japan in phases. 1,038 were kept behind for war crimes trials; 969 would be found guilty, and 236 would be given death sentences.
ww2dbaseOn 17 Aug 1945, Sukarno declared an independent Indonesia, and the constitution was approved by the Preparatory Committee for the Independence of Indonesia on the following day. On 27 Oct, the Battle of Surabaya broke out between Indonesian nationalists and British and Dutch forces, the first major action in what was to become a four-year long war for independence. On 27 Dec 1949, the war ended with the Dutch-Indonesian Round Table Conference, with the Dutch ceding control of the majority of the former Dutch East Indies to the Republic of the United States of Indonesia. The member nations would dissolve themselves into the Republic of Indonesia by the end of 1950, forming the Indonesian nation today.
ww2dbaseThe western half of New Guinea remained under Dutch control as Dutch New Guinea. In the 1950s, the Dutch prepared the territory for full independence, and held elections in 1959 for the New Guinea Council. On 1 Oct 1962, the Netherlands handed the territory over to the United Nations Temporary Executive Authority. On 1 May 1963, control was given to Indonesia, who renamed the western half of New Guinea as West Irian and later Irian Jaya. In 1969, a referendum was held, the result of which made Irian Jaya officially a part of Indonesia.
ww2dbaseSource: Wikipedia
Last Major Update: Jun 2011
| Events Taken Place in Dutch East Indies | ||
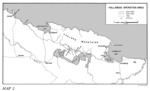
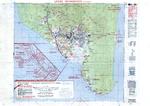
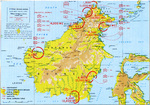
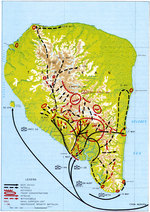
| Dutch East Indies Campaign, Borneo | 15 Dec 1941 - 1 Apr 1942 | |
| Dutch East Indies Campaign, Celebes and Moluccas | 11 Jan 1942 - 31 Jul 1942 | |
| Dutch East Indies Campaign, Java | 4 Feb 1942 - 31 Mar 1942 | |
| Dutch East Indies Campaign, Sumatra | 13 Feb 1942 - 28 Mar 1942 | |
| New Guinea-Papua Campaign, Phase 2 | 8 Mar 1942 - 4 Mar 1943 | |
| New Guinea-Papua Campaign, Phase 3 | 30 Sep 1943 - 23 May 1945 | |
| Operation Cockpit and Operation Transom | 19 Apr 1944 - 17 May 1944 | |
| Battle of Morotai | 15 Sep 1944 - 14 Jan 1945 | |
| Facilities | ||
| Hollandia Airfield Complex | Air Base | |
| Hotel Yamato | Military Headquarters | |
Photographs
 |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |
Dutch East Indies in World War II Interactive Map
Please consider supporting us on Patreon. Even $1 per month will go a long way! Thank you. Please help us spread the word: Stay updated with WW2DB: |
Visitor Submitted Comments
15 Nov 2013 02:09:04 AM
The Post-war United States of Indonesia was inherently unstable, encompassing 100 million ethnically and religiously diverse people on 10,000 islands, many of whom had no wish to exchange rule from the Hague for rule from Batavia. Sukharno's expansionist ambitions and tolerance of communism eventually fueled U.S. hostility to the nationalist Dictatorship that Washington had placed in power with threats to withdrawing American aid to the Netherlands; resulting finally in the CIA supporting his opponents with training, organisation and payment of mercenaries when they staged an abortive rebellion in Sumatra and Celebes in February 1958.
21 Nov 2013 11:35:28 AM
- On 17 Aug 1945, Sukarno declared an independent Indonesia.
- On 10 Nov 1945, the Battle of Surabaya
2 Oct 2016 09:50:24 PM
My father-in-law was a Dutch civilian prisoner of war in Indonesia during WWII. Is there a data base where we could find his name and prison camp?
24 Apr 2017 01:31:46 AM
my father, uncle, grandmother were dutch civilians & my grandfather was in the dutch marines, they were all in p.o.w. camps. How do i find out more information about them & where they were?
3 May 2017 01:04:02 AM
MY FATHER AND MY UNCLE SERVED THE DUTCH ARMY OR MARINES.MY FATHER HELP TO SUPPORT THE POW HE ENTER AS SPY INTO JAPANESE PRISON BY BROUGHT MEDICATIONS AND NEWS THAT GIVES HOPE TO THE POW SUCH AS DUTCH OR DUTCH INDONESIAN WHO WAS THE POW.PLEASE IF YOU CANFIND LIST OF MY FAMILY CENTIAGO FROM CELEBES MAKASSAR FROM THE WORLD WAR TWO.THANK YOU VERY MUCH ,JACKY CENTIAGO
10 Aug 2017 09:52:39 PM
I have a relative that was in the Korps Insulinde (1942–1945). Is there somewhere that I can get a military record? list of names?
22 Nov 2017 04:26:20 PM
My great grandfather died in Bandung in 1953 as 'slachtoffer van de oorlog'. He was in the Dutch Army. My grandfather was born in 1916 in Batavia, assuming during my great grandfather's service. Is there anywhere where we can confirm
15 Feb 2020 07:33:52 AM
Mammie's Journal of My Childhood includes the Mother's journal and the daughter's memories of their internment in the Japanese camps in Brastagi and Palembag during World War II. As Jolanthe Zelling translated, Jeanne Tuttle edited the journal and Jolly's memories into book form.
16 Feb 2020 03:40:27 PM
Sukarno declared Indonesia as indenpendent nation in august 17 1945
All visitor submitted comments are opinions of those making the submissions and do not reflect views of WW2DB.
- » WW2DB's 20th Anniversary (29 Dec 2024)
- » Wreck of USS Edsall Found (14 Nov 2024)
- » Autumn 2024 Fundraiser (7 Nov 2024)
- » Nobel Peace Prize for the Atomic Bomb Survivors Organization (11 Oct 2024)
- » See all news
 |
- » 1,151 biographies
- » 337 events
- » 44,186 timeline entries
- » 1,243 ships
- » 350 aircraft models
- » 207 vehicle models
- » 375 weapon models
- » 123 historical documents
- » 260 facilities
- » 470 book reviews
- » 28,668 photos
- » 431 maps
Thomas Dodd, late 1945
Please consider supporting us on Patreon. Even $1 a month will go a long way. Thank you!
Or, please support us by purchasing some WW2DB merchandise at TeeSpring, Thank you!
9 Oct 2011 01:47:01 AM
Thank you Peter Chen,
I am 84 years old and was one of the Dutch citizens who was one of the warvictims in the former D.E.I. during the Japanese occupation 1942-1945. My father was killed by the Kempeitai. Please read my website: www.dutch-east-indies.com
Greetings from Holland, Elizabeth